Learn C : What are Preprocessor Directive , Introduction , Examples ,Interview Questions and Many More.
The C Preprocessor is a micro processor which is used in the pre-compilation process to check the program before the actual compilation can be done.
It is called microprocessor because it allows us to add macros in our program.
Each preprocessor directive can start with # symbol.

Use of preprocessor Directives :
It makes the developer to read the program easily.
It makes modification of program easy.
It makes the program architecture independent.
Types of Preprocessor Directives:
File Inclusive Directive:
The files which are declared inside the Header Files can be used if once declared in the program.
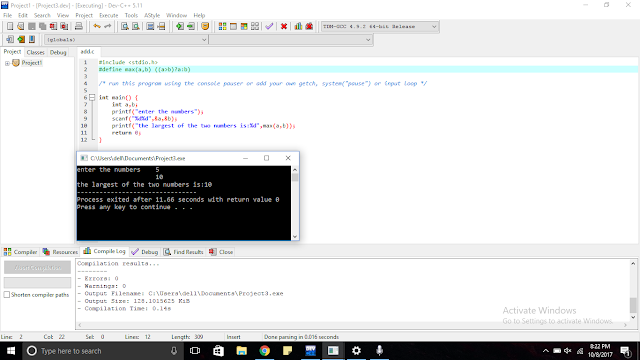
Example: To print the sum of two numbers.
Macro Substitution directive:
This directive can be used to denote constant values, the constant values can be of any data type.
The #define is a macro.
Example: Print the largest of the two numbers : The macro works internally as ternary operator.
Conditional Directive:
In this directive set of statements can be included or excluded on the basis of conditions in the main program.
Example: ➣ Below is the example of if, else, endif.
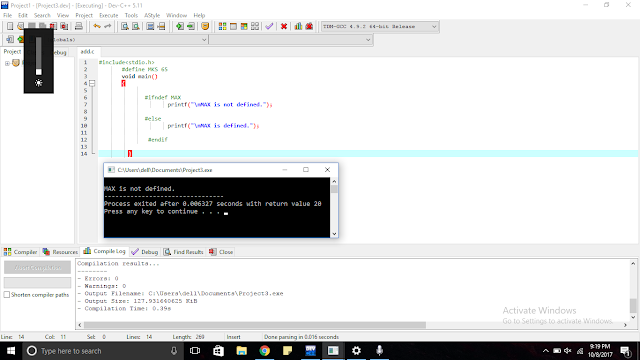
➣ ifdef, else, endif
➣ if, elif, else, endif : It is similar to if-else ladder statement.
➣ indef : It is used to check whether the macro name is previously defined or not.
Undefines a symbol specified by <identifier> which was previously defined with a #define directive.
- #undef Directive is used to undefine any Macro Symbol.
- #undef can undefine only “User Defined” Macro’s.
- #undef cannot undefine “Global Macro Identifiers“.
- #undef is used where we have to redefine any Macro Identifier.
Miscellaneous Directive:
➣ # Line : It is used to overwrite the default value of pre-defined macro- names __LINE__ and __FILE__. By default __LINE__ displays the current line number and __FILE__ displays the current filename.
Example 1: Default value of #Line
Example 2: Overwrite the default value of #Line
But note that the printf line must be in the the same line of void main( ) for the correct output otherwise the line number output will be different from your macro definition as shown below:
➣ # error : It is used to force the compile to stop compiling the source code. In other words we can manually force the compiler to stop compiling and give fatal error.
➣ #pragma : #pragma once is used to include the header file only once.
C Preprocessor Interview Questions:
- What is the difference between #include "filename" vs #include <filename>?
- What is the use of #define?
- Can a #define use a string character as replacement text?
- Can you give an example of #define?
- Can you give an example of #define with a Macro?
- What are Preprocessor Directives?
- How can you avoid including a header more than once?
- Can a file other than a .h file be included with #include?The preprocessor will include whatever file you specify in your #include statement. Therefore, if you have the line#include <macros.inc>in your program, the file macros.inc will be included in your precompiled program. It is, however, unusual programming practice to put any file that does not have a .h or .hpp extension in an #include statement. You should always put a .h extension on any of your C files you are going to include. This method makes it easier for you and others to identify which files are being used for preprocessing purposes.
For any query related to the content mail to devkumar082001@gmail.com























No comments: